Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE G49108TO
G49108TO
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G49108TO
- IUPAC Condensed
- GlcNAc(b1-
External Links
- GlyConnect structure
- GlyGen
- ChEBI
- PubChem Compound
- PubChem Substance
- The Human Metabolome Database
- CarbBank
- 9 3780 3968 4708 25653 28493 29021 29527 29549 31775 32028 32903 33539 36048 36270 37035 37525 37675 37677 37678 39452 39454 39456 39609 39611 39613 39614 40149 40150 40151 40355 40591 40600 42059 42207 42220 43184 43893 43925 43926 43931 43932 43941 44395 44396 44397 44549 46453 47268 47468 47537 47603 47796 48630 48812 48813 49006 49732 50589 50736
3D Structures
- GLYCAM
- DGlcpNAcb1-OH
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |
| Sus scrofa (pig) | |
| Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B4GALT5 | (not applicable) |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-S-pNP |
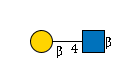 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-S-pNP | |
| B4GALT1 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
R |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
R | |
| B4GALT2 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
Benzyl-[beta] |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
Benzyl-[beta] | |
| B3GALT2 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
Lemieux |
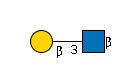 G00056MO
G00056MO
|
Lemieux | |
| B3GALT5 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
R |
 G00056MO
G00056MO
|
R |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B4GALT5 | (not applicable) |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-S-pNP |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-S-pNP | |
| B4GALT4 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-1-thio-p-Nitrophenyl |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-1-thio-p-Nitrophenyl | |
| B4GALT3 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
4-Me-lumbelyl-[beta] |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
4-Me-lumbelyl-[beta] | |
| B4GALT4 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-1-4-methyl-umbelliferyl |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-1-4-methyl-umbelliferyl | |
| B4GALT1 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
Core Protein
GlycoEpitope
- Epitope ID
- EP0004
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| E.coli O4-H5 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O4-K52 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O40 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O41 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O42 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O45rel | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O48 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O53 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O55 | Escherichia coli |
| E.coli O56 | Escherichia coli |
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:b-dglc-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2122h-1b_1-5_2*NCC/3=O]/1/
Literature
| PubMed ID | Title | First Author | Publication Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 37422472 | The structural pathology for hypophosphatasia caused by malfunctional tissue non-specific alkaline phosphatase | Yu Y | 2023 Jul 08 |
|
| 37446392 | Identification of Regulatory Molecular “Hot Spots” for LH/PLOD Collagen Glycosyltransferase Activity | Mattoteia D | 2023 Jul 07 |
|
| 37390815 | Glucose-induced CRL4COP1-p53 axis amplifies glycometabolism to drive tumorigenesis | Su Y | 2023 Jul 06 |
|
| 37409796 | Efficient Production of N-Acetylneuraminic Acid in Escherichia coli Based on the UDP-N-Acetylglucosamine Biosynthetic Pathway | Zhao M | 2023 Jul 06 |
|
| 37357620 | Crystal structures of Na+,K+‐ATPase reveal the mechanism that converts the K+‐bound form to Na+‐bound form and opens and closes the cytoplasmic gate | Kanai R | 2023 Jul 06 |
|
| 37407593 | Structure of engineered hepatitis C virus E1E2 ectodomain in complex with neutralizing antibodies | Metcalf MC | 2023 Jul 05 |
|
| 37400538 | Discovery of VH domains that allosterically inhibit ENPP1 | Solomon PE | 2023 Jul 03 |
|
| 37395731 | Author response: Sterol derivative binding to the orthosteric site causes conformational changes in an invertebrate Cys-loop receptor | De Gieter S | 2023 Jul 03 |
|
| 37224467 | O-linked N-acetylglucosamine modification is essential for physiological adipose expansion induced by high-fat feeding | Nakamoto A | 2023 Jul 01 |
|
| 37028871 | Elucidating the role of N-acetylglucosamine in Group A Carbohydrate for the development of an effective glycoconjugate vaccine against Group A Streptococcus | Pitirollo O | 2023 Jul 01 |
|
 G14843DJ
G14843DJ
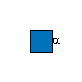 G68544GH
G68544GH
