Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE
 Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10
Disintegrin and metalloproteinase domain-containing protein 10
Summary
- UniProt ID
- O14672
- Gene Symbol
-
- ADAM10
- KUZ
- MADM
- Gene ID
- 102
- Organism
- Homo sapiens (human)
Annotation
- Keyword
-
- 3D-structure
- Alternative splicing
- Alzheimer disease
- Amyloidosis
- Cell junction
- Cell membrane
- Cell projection
- Cleavage on pair of basic residues
- Cytoplasm
- Cytoplasmic vesicle
- Direct protein sequencing
- Disease variant
- Disulfide bond
- Glycoprotein
- Golgi apparatus
- Metal-binding
- Metalloprotease
- Neurodegeneration
- Notch signaling pathway
- Phosphoprotein
- Reference proteome
- SH3-binding
- Signal
- Transmembrane helix
- Zinc
- Zymogen
- Gene Ontology (GO)
| GO Term |
|---|
| Golgi apparatus |
| Golgi-associated vesicle |
| adherens junction |
| cell surface |
| clathrin-coated vesicle |
| perinuclear endoplasmic reticulum |
| focal adhesion |
| postsynaptic density |
| extracellular exosome |
| pore complex |
Sequence
MVLLRVLILLLSWAAGMGGQYGNPLNKYIRHYEGLSYNVDSLHQKHQRAKRAVSHEDQFLRLDFHAHGRHFNLRMKRDTSLFSDEFKVETSNKVLDYDTSHIYTGHIYGEEGSFSHGSVIDGRFEGFIQTRGGTFYVEPAERYIKDRTLPFHSVIYHEDDINYPHKYGPQGGCADHSVFERMRKYQMTGVEEVTQIPQEEHAANGPELLRKKRTTSAEKNTCQLYIQTDHLFFKYYGTREAVIAQISSHVKAIDTIYQTTDFSGIRNISFMVKRIRINTTADEKDPTNPFRFPNIGVEKFLELNSEQNHDDYCLAYVFTDRDFDDGVLGLAWVGAPSGSSGGICEKSKLYSDGKKKSLNTGIITVQNYGSHVPPKVSHITFAHEVGHNFGSPHDSGTECTPGESKNLGQKENGNYIMYARATSGDKLNNNKFSLCSIRNISQVLEKKRNNCFVESGQPICGNGMVEQGEECDCGYSDQCKDECCFDANQPEGRKCKLKPGKQCSPSQGPCCTAQCAFKSKSEKCRDDSDCAREGICNGFTALCPASDPKPNFTDCNRHTQVCINGQCAGSICEKYGLEECTCASSDGKDDKELCHVCCMKKMDPSTCASTGSVQWSRHFSGRTITLQPGSPCNDFRGYCDVFMRCRLVDADGPLARLKKAIFSPELYENIAEWIVAHWWAVLLMGIALIMLMAGFIKICSVHTPSSNPKLPPPKPLPGTLKRRRPPQPIQQPQRQRPRESYQMGHMRR
Glycosylation Sites
| Position | Description | PubMed ID | GlyTouCan ID | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 31 |
|
|||
| 36 |
|
|||
| 37 |
|
|
||
| 124 |
|
|||
| 130 |
|
|||
| 194 |
|
|||
| 248 |
|
|||
| 267 | N-linked (GlcNAc...) asparagine | |||
| 269 |
|
|||
| 278 | N-linked (GlcNAc...) asparagine |
Feature
 : Glycosylation Site from GlyGen
: Glycosylation Site from GlyGen : Glycosylation Site from UniProt
: Glycosylation Site from UniProt
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Activated NOTCH1 Transmits Signal to the Nucleus | Homo sapiens |
| Amyloid fiber formation | Homo sapiens |
| Collagen degradation | Homo sapiens |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD Domain Mutants | Homo sapiens |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 HD+PEST Domain Mutants | Homo sapiens |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 PEST Domain Mutants | Homo sapiens |
| Constitutive Signaling by NOTCH1 t(7;9)(NOTCH1:M1580_K2555) Translocation Mutant | Homo sapiens |
| Degradation of the extracellular matrix | Homo sapiens |
| EPH-ephrin mediated repulsion of cells | Homo sapiens |
| NOTCH2 Activation and Transmission of Signal to the Nucleus | Homo sapiens |
Disease
| DO ID | Disease Name | Source |
|---|---|---|
| DOID:0060258 | reticulate acropigmentation of Kitamura | |
| DOID:0110050 | Alzheimer's disease 18 |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
 G43417UB
G43417UB
 G49108TO
G49108TO
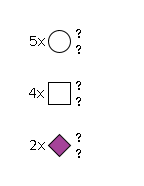 G00912UN
G00912UN
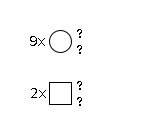 G80920RR
G80920RR
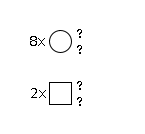 G62765YT
G62765YT
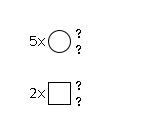 G02815KT
G02815KT
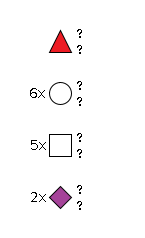 G57776ZS
G57776ZS
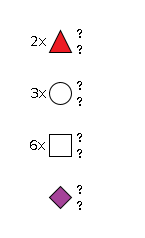 G20706XG
G20706XG
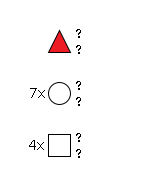 G15664MX
G15664MX
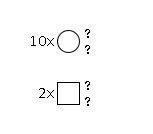 G83460ZZ
G83460ZZ
 G70223PD
G70223PD
 G46503DX
G46503DX
 G25079LO
G25079LO
 G70101JE
G70101JE
 G90659AW
G90659AW
 G64527OM
G64527OM
 G31852PQ
G31852PQ
 G41247ZX
G41247ZX
 G92050GC
G92050GC
 G28681TP
G28681TP
