Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE G49108TO
G49108TO
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G49108TO
- IUPAC Condensed
- GlcNAc(b1-
External Links
- GlyConnect structure
- GlyGen
- ChEBI
- PubChem Compound
- PubChem Substance
- The Human Metabolome Database
- CarbBank
- 9 3780 3968 4708 25653 28493 29021 29527 29549 31775 32028 32903 33539 36048 36270 37035 37525 37675 37677 37678 39452 39454 39456 39609 39611 39613 39614 40149 40150 40151 40355 40591 40600 42059 42207 42220 43184 43893 43925 43926 43931 43932 43941 44395 44396 44397 44549 46453 47268 47468 47537 47603 47796 48630 48812 48813 49006 49732 50589 50736
3D Structures
- GLYCAM
- DGlcpNAcb1-OH
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Streptococcus pneumoniae | |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |
| Sus scrofa (pig) | |
| Rattus norvegicus (Norway rat) |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B4GALT5 | (not applicable) |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-S-pNP |
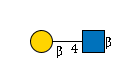 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-S-pNP | |
| B4GALT1 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
R |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
R | |
| B4GALT2 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
Benzyl-[beta] |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
Benzyl-[beta] | |
| B3GALT2 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
Lemieux |
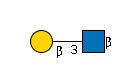 G00056MO
G00056MO
|
Lemieux | |
| B3GALT5 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
R |
 G00056MO
G00056MO
|
R |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B4GALT5 | (not applicable) |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-S-pNP |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-S-pNP | |
| B4GALT4 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-1-thio-p-Nitrophenyl |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-1-thio-p-Nitrophenyl | |
| B4GALT3 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
4-Me-lumbelyl-[beta] |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
4-Me-lumbelyl-[beta] | |
| B4GALT4 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
[beta]-1-4-methyl-umbelliferyl |
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
[beta]-1-4-methyl-umbelliferyl | |
| B4GALT1 | UDP-Gal |
 G49108TO
G49108TO
|
 G00055MO
G00055MO
|
Core Protein
GlycoEpitope
- Epitope ID
- EP0004
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Antimicrobial peptides | Sus scrofa |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Rattus norvegicus |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Dictyostelium discoideum |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Bos taurus |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Canis familiaris |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Mus musculus |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Gallus gallus |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Homo sapiens |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Drosophila melanogaster |
| Antimicrobial peptides | Xenopus tropicalis |
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:b-dglc-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2122h-1b_1-5_2*NCC/3=O]/1/
Literature
| PubMed ID | Title | First Author | Publication Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36124412 | Hexosamine pathway activation improves memory but does not extend lifespan in mice | Allmeroth K | 2022 Sep 19 |
|
| 36115831 | Structural mechanism of tapasin-mediated MHC-I peptide loading in antigen presentation | Jiang J | 2022 Sep 17 |
|
| 35971553 | Engineering SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies for increased potency and reduced viral escape pathways | Zhao F | 2022 Sep 16 |
|
| 36103542 | Design of the SARS-CoV-2 RBD vaccine antigen improves neutralizing antibody response | Dickey TH | 2022 Sep 16 |
|
| 36109732 | A potent synthetic nanobody with broad-spectrum activity neutralizes SARS-CoV-2 virus and the Omicron variant BA.1 through a unique binding mode | Zhao D | 2022 Sep 15 |
|
| 36106687 | Crystal structure and sugar-binding ability of the C-terminal domain of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase IV establish a new carbohydrate-binding module family | Oka N | 2022 Sep 15 |
|
| 36104594 | The value of injectable viscoelastic supplements for joints | Bowden DJ | 2022 Sep 14 |
|
| 36104770 | O-GlcNAcylation: an important post-translational modification and a potential therapeutic target for cancer therapy | Lu Q | 2022 Sep 14 |
|
| 35952670 | Allelic polymorphism controls autoreactivity and vaccine elicitation of human broadly neutralizing antibodies against influenza virus | Sangesland M | 2022 Sep 13 |
|
| 35977542 | Vaccination with a structure-based stabilized version of malarial antigen Pfs48/45 elicits ultra-potent transmission-blocking antibody responses | McLeod B | 2022 Sep 13 |
|
 G14843DJ
G14843DJ
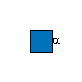 G68544GH
G68544GH
