Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE G57321FI
G57321FI
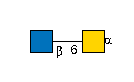
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G57321FI
- IUPAC Condensed
- GalNAc(a1-
- Motifs
- Tn antigen
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Ovis aries (sheep) | |
| Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) | |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | |
| Bos taurus (domestic cattle) | |
| Escherichia coli |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
root
cellular organisms [inference]
Eukaryota (eucaryotes) [inference]
Opisthokonta [inference]
Metazoa (metazoans) [inference]
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
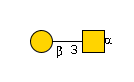 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
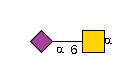 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis | |
| B3GNT6 | UDP-GlcNAc |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[alpha]-pNP |
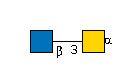 G00035MO
G00035MO
|
[alpha]-pNP |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
benzyl | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GALNAC3 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GAL2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
para-nitrophenol | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[alpha]-Bz | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
KEGG BRITE Database
Core Protein
| UniProt ID | Protein Name | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| O75460 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase/endoribonuclease IRE1 | ||
| O75462 | Cytokine receptor-like factor 1 | ||
| O75487 | Glypican-4 | ||
| O75509 | Tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 21 | ||
| O75752 | UDP-GalNAc:beta-1,3-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 | ||
| O75882 | Attractin | ||
| O75976 | Carboxypeptidase D | ||
| O76061 | Stanniocalcin-2 | ||
| O94766 | Galactosylgalactosylxylosylprotein 3-beta-glucuronosyltransferase 3 | ||
| O94856 | Neurofascin |
GlycoEpitope
- Epitope ID
- EP0021
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Ficolins bind to repetitive carbohydrate structures on the target cell surface | Sus scrofa |
| Initial triggering of complement | Mus musculus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Gallus gallus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Xenopus tropicalis |
| Initial triggering of complement | Sus scrofa |
| Initial triggering of complement | Bos taurus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Canis familiaris |
| Initial triggering of complement | Rattus norvegicus |
| Initial triggering of complement | Homo sapiens |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Bos taurus |
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:a-dgal-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2112h-1a_1-5_2*NCC/3=O]/1/
Literature
| PubMed ID | Title | First Author | Publication Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 29665849 | An innovative immunotherapeutic strategy for ovarian cancer: CLEC10A and glycomimetic peptides | Eggink LL | 2018 Apr 17 |
|
| 29894213 | Low-glycosylated forms of both FSH and LH play major roles in the natural ovarian stimulation | Wide L | 2018 Apr 03 |
|
| 28774839 | pH-labile PEGylation of siRNA-loaded lipid nanoparticle improves active targeting and gene silencing activity in hepatocytes | Hashiba K | 2017 Sep 28 |
|
| 28922551 | Lectin BS‐I inhibits cell migration and invasion via AKT/GSK‐3β/β‐catenin pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma | Jian Q | 2017 Sep 18 |
|
| 28981809 | Impact of enhanced metabolic stability on pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of GalNAc–siRNA conjugates | Nair JK | 2017 Sep 15 |
|
| 28785176 | Predicting the Retention Behavior of Specific O-Linked Glycopeptides | Badgett MJ | 2017 Sep |
|
| 29069408 | Asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 mediates productive uptake of N-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated and unconjugated phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides into liver hepatocytes | Tanowitz M | 2017 Oct 23 |
|
| 28709621 | Role of N-acetyl galactosamine-4-SO4, a ligand of CD206 in HSV-induced mouse model of Behçet's disease | Choi B | 2017 Oct 15 |
|
| 28921968 | Automated Solid-Phase Click Synthesis of Oligonucleotide Conjugates: From Small Molecules to Diverse N-Acetylgalactosamine Clusters | Farzan VM | 2017 Oct 04 |
|
| 28986168 | Highly specific delivery of siRNA to hepatocytes circumvents endothelial cell-mediated lipid nanoparticle-associated toxicity leading to the safe and efficacious decrease in the hepatitis B virus | Sato Y | 2017 Nov 28 |
|
PubAnnotation
 G00041MO
G00041MO
