Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
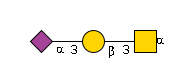
MIRAGE G65562ZE
G65562ZE
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G65562ZE
- IUPAC Condensed
- Neu5Ac(a2-3)Gal(b1-3)GalNAc(a1-
- Motifs
- Sialyl T antigen
- Subsumption Level
- Fully-defined saccharide
- Monoisotopic Mass
- 674.24
External Links
3D Structures
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | |
| Canis lupus familiaris (dog) | |
| Danio rerio (zebrafish) | |
| Saccharomyces cerevisiae (brewer's yeast) | |
| Sus scrofa (pig) |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
root
cellular organisms [inference]
Eukaryota (eucaryotes) [inference]
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
Ser/Thr |
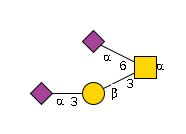 G01614ZM
G01614ZM
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST3GAL4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
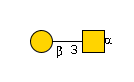 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
free |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
free | |
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
R |
 G01614ZM
G01614ZM
|
R | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
Ser/Thr |
 G01614ZM
G01614ZM
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST3GAL2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
R |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
R |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
Ser/Thr |
 G01614ZM
G01614ZM
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST3GAL4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Antifreeze glycoprotein |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
Antifreeze glycoprotein | |
| ST3GAL2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
|||
| ST3GAL4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
free |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
free | |
| ST3GAL1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
free |
 G65562ZE
G65562ZE
|
free |
KEGG BRITE Database
Core Protein
| UniProt ID | Protein Name | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| D9N008 | Epiglycanin | ||
| P00743 | Coagulation factor X | ||
| P00747 | Plasminogen | ||
| P01215 | Glycoprotein hormones alpha chain | ||
| P01588 | Erythropoietin | ||
| P01824 | Immunoglobulin heavy variable 4-39 | ||
| P01876 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant alpha 1 | ||
| P01880 | Immunoglobulin heavy constant delta | ||
| P02656 | Apolipoprotein C-III | ||
| P02668 | Kappa-casein |
GlycomeAtlas
Tissues in which this glycan is expressed are highlighted in yellow.
- Danio rerio
Literature
- Tissue
-
- heart
- intestine
- liver
- Reference
- Yamakawa N et al. Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):4647. Published 2018 Nov 7. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-06950-3
- DOI
- 10.1038/s41467-018-06950-3
Localization sites organized by hierarchy by Uber-anatomy ontology (UBERON)
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:a-dgal-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl 3b:b-dgal-HEX-1:5 4b:a-dgro-dgal-NON-2:6|1:a|2:keto|3:d 5s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n 2:1o(3+1)3d 3:3o(3+2)4d 4:4d(5+1)5n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/3,3,2/[a2112h-1a_1-5_2*NCC/3=O][a2112h-1b_1-5][Aad21122h-2a_2-6_5*NCC/3=O]/1-2-3/a3-b1_b3-c2
Literature
| PubMed ID | Title | First Author | Publication Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 35585145 | Origins of glycan selectivity in streptococcal Siglec-like adhesins suggest mechanisms of receptor adaptation | Bensing BA | 2022 May 18 |
|
| 34191522 | The O-Glycome of Human Nigrostriatal Tissue and Its Alteration in Parkinson's Disease | Wilkinson H | 2021 Aug 6 |
|
| 32820052 | Tandem sialoglycan-binding modules in a Streptococcus sanguinis serine-rich repeat adhesin create target dependent avidity effects | Stubbs HE | 2020 Oct 23 |
|
| 32236654 | Colorectal cancer cell lines show striking diversity of their O-glycome reflecting the cellular differentiation phenotype | Madunic K | 2020 Mar 31 |
|
| 30405127 | Systems glycomics of adult zebrafish identifies organ-specific sialylation and glycosylation patterns | Yamakawa N | 2018 Nov 07 |
|
| 27685666 | Structures of the Streptococcus sanguinis SrpA Binding Region with Human Sialoglycans Suggest Features of the Physiological Ligand | Loukachevitch LV | 2016 Oct 11 |
|
| 23001782 | Micro- and macroheterogeneity of N-glycosylation yields size and charge isoforms of human sex hormone binding globulin circulating in serum | Sumer-Bayraktar Z | 2012 Nov |
|
| 21765814 | A Structural Model for Binding of the Serine-Rich Repeat Adhesin GspB to Host Carbohydrate Receptors | Pyburn TM | 2011 Jul 07 |
|
| 16169874 | Molecular Cloning and Expression of Human ST6GalNAc III: Restricted Tissue Distribution and Substrate Specificity | Tsuchida A | 2005 Sep 01 |
|
| 15557177 | The Glycosylation of Human Serum IgD and IgE and the Accessibility of Identified Oligomannose Structures for Interaction with Mannan-Binding Lectin | Arnold JN | 2004 Dec 01 |
|
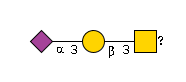 G72008IY
G72008IY
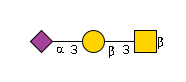 G02684WR
G02684WR
