Submissions






GlyTouCan
Glycan Structure Repository
GlyComb
Glycoconjugate Repository
GlycoPOST
Glycomics MS raw data RepositoryUniCarb-DR
Glycomics MS Repository for glycan annotations from GlycoWorkbench
LM-GlycoRepo
Repository for lectin-assisted multimodality dataAll Resources
Genes / Proteins / Lipids Glycans / Glycoconjugates Glycomes Pathways / Interactions / Diseases / OrganismsTools
Guidelines
MIRAGE G57321FI
G57321FI
Summary
- GlyTouCan ID
-
G57321FI
- IUPAC Condensed
- GalNAc(a1-
- Motifs
- Tn antigen
External Links
- GlyConnect structure
- GlyGen
- ChEBI
- PubChem Compound
- PubChem Substance
- The Human Metabolome Database
- CarbBank
-
- 6
- 7
- 2184
- 2185
- 2186
- 2187
- 3470
- 3659
- 3733
- 5034
- 10921
- 10922
- 10923
- 30785
- 30918
- 31592
- 32839
- 32957
- 33178
- 33218
- 33468
- 33887
- 33913
- 34825
- 34838
- 34841
- 34985
- 35031
- 35036
- 35106
- 35261
- 35803
- 35831
- 35944
- 35992
- 36198
- 36249
- 36835
- 37727
- 37767
- 37769
- 37922
- 37939
- 37952
- 38122
- 38186
- 38193
- 38196
- 38206
- 38207
- 38208
- 38561
- 38638
- 38698
- 40629
- 41864
- 42206
- 42380
- 42739
- 42792
- 43909
- 43910
- 43916
- 43917
- 43918
- 43920
- 43922
- 43930
- 43948
- 44243
- 44374
- 44492
- 44493
- 44506
- 45605
- 45638
- 45778
- 45883
- 45890
- 46467
- 46557
- 46860
- 47103
- 47105
- 47107
- 47180
- 47181
- 47182
- 47328
- 47385
- 48045
- 48233
- 48245
- 49041
- 49508
- 49665
- 49666
- 50468
Organisms
| Organisms | Evidence |
|---|---|
| Ovis aries (sheep) | |
| Cricetulus griseus (Chinese hamster) | |
| Mus musculus (house mouse) | |
| Bos taurus (domestic cattle) | |
| Escherichia coli |
Taxonomic Hierarchy
root
cellular organisms [inference]
Eukaryota (eucaryotes) [inference]
Opisthokonta [inference]
Metazoa (metazoans) [inference]
GlycoGene Database (GGDB)
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
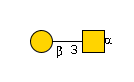 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
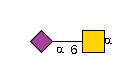 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis | |
| B3GNT6 | UDP-GlcNAc |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[alpha]-pNP |
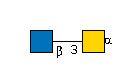 G00035MO
G00035MO
|
[alpha]-pNP |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Product | Reducing terminal(Product) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1GALT1 | (not applicable) |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G00031MO
G00031MO
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GALNAC4 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
benzyl | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
O-glycan Synthesis |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
O-glycan Synthesis | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 |
 G36123IU
G36123IU
|
[Ala-Thr(*)-Ala]2-7 |
| Gene Symbol | Donor | Acceptor | Reducing terminal(Acceptor) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ST6GALNAC3 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr | |
| ST6GAL2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
para-nitrophenol | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
benzyl | |
| ST6GALNAC1 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
[alpha]-Bz | |
| ST6GALNAC2 | CMP-Neu5Ac |
 G57321FI
G57321FI
|
Ser/Thr |
KEGG BRITE Database
Core Protein
| UniProt ID | Protein Name | Reference | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Q9Y2G1 | Myelin regulatory factor | ||
| Q9Y4C4 | Malignant fibrous histiocytoma-amplified sequence 1 | ||
| Q9Y4L1 | Hypoxia up-regulated protein 1 | ||
| Q9Y520 | Protein PRRC2C | ||
| Q9Y5L2 | Hypoxia-inducible lipid droplet-associated protein | ||
| Q9Y5M8 | Signal recognition particle receptor subunit beta | ||
| Q9Y5T4 | DnaJ homolog subfamily C member 15 | ||
| Q9Y5X9 | Endothelial lipase | ||
| Q9Y5Y6 | Suppressor of tumorigenicity 14 protein | ||
| Q9Y5Z0 | Beta-secretase 2 |
GlycoEpitope
- Epitope ID
- EP0021
Pathway
| Pathway Name | Organism |
|---|---|
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Bos taurus |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Rattus norvegicus |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Mus musculus |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Homo sapiens |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Xenopus tropicalis |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Gallus gallus |
| Lectin pathway of complement activation | Canis familiaris |
Sequence Descriptors
- GlycoCT
-
RES 1b:a-dgal-HEX-1:5 2s:n-acetyl LIN 1:1d(2+1)2n
- WURCS
- WURCS=2.0/1,1,0/[a2112h-1a_1-5_2*NCC/3=O]/1/
Literature
| PubMed ID | Title | First Author | Publication Date | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 36293310 | Mutation Hotspot for Changing the Substrate Specificity of β-N-Acetylhexosaminidase: A Library of GlcNAcases | Nekvasilová P | 2022 Oct 18 |
|
| 36094307 | Disruption of the tagF Orthologue in the epa Locus Variable Region of Enterococcus faecalis Causes Cell Surface Changes and Suppresses an eep -Dependent Lysozyme Resistance Phenotype | Rouchon CN | 2022 Oct 18 |
|
| 35987426 | Differential expression of glycans in the urothelial layers of horse urinary bladder | Desantis S | 2022 Oct |
|
| 36253014 | Metabolomic markers of glucose regulation after a lifestyle intervention in prediabetes | Sevilla-Gonzalez MDR | 2022 Oct |
|
| 36041884 | Plasma and Liver Pharmacokinetics of the N-Acetylgalactosamine Short Interfering RNA JNJ-73763989 in Recombinant Adeno-Associated–Hepatitis B Virus–Infected Mice | Sandra L | 2022 Oct |
|
| 35907378 | Mn-doped bimetallic synergistic catalysis boosts for enzymatic phosphorylation of N-Acetylglucosamine/ N-Acetylgalactosamine and their derivatives | Xu H | 2022 Nov |
|
| 35618750 | Author Correction: The Pel polysaccharide is predominantly composed of a dimeric repeat of α-1,4 linked galactosamine and N-acetylgalactosamine | Le Mauff F | 2022 May 26 |
|
| 35504880 | Structural basis for the synthesis of the core 1 structure by C1GalT1 | González-Ramírez AM | 2022 May 03 |
|
| 35321541 | Protein Engineering of PhUGT, a Donor Promiscuous Glycosyltransferase, for the Improved Enzymatic Synthesis of Antioxidant Quercetin 3-O-N-Acetylgalactosamine | Xu Z | 2022 Mar 24 |
|
| 35151686 | Loss of the N-acetylgalactosamine side chain of the GPI-anchor impairs bone formation and brain functions and accelerates the prion disease pathology | Hirata T | 2022 Mar |
|
PubAnnotation
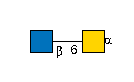 G00041MO
G00041MO
